Laser Cutting
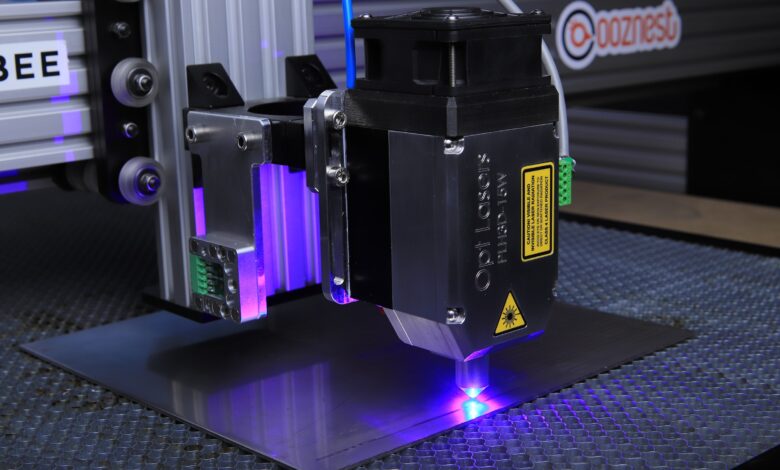
Laser cutting is a technology that uses a laser to cut materials and is typically used for industrial manufacturing applications. Still, it is also starting to be used by schools, small businesses, and hobbyists. Laser cutting works by directing the output of a high-power laser at the material to be cut. The material then melts, burns, vaporizes or is blown away by a jet of gas, leaving a clean edge.
Laser cutting is a highly versatile technology that cuts various materials, including metal, wood, plastic, glass, and even stone. It can create simple and complex shapes, making it ideal for everything from prototyping to full-scale production.
How Does Laser Cutting Work?
Laser cutting works by directing a high-powered laser at the material to be cut. The material is melted, burned, vaporized, or blown away by a gas jet, leaving a clean edge.
There are three main types of laser cutting: CO2, fiber, and crystal. CO2 lasers are the most common type of laser cutter, and they can be used to cut various materials, including metal, wood, plastic, glass, and stone. Fiber lasers are becoming increasingly popular for cutting metals, as they offer higher precision and speed than CO2 lasers. Crystal lasers are the most potent laser cutter type but are also the most expensive.
Laser Cutting Machine
Laser cutting machine come in various sizes and power levels to suit various applications. Low-power desktop units are ideal for small-scale projects, while high-power industrial machines can be used for large-scale production.
CO2 laser cutters are the most common machine available at various power levels. Fiber laser cutters are becoming increasingly popular for cutting metals, offering higher precision and speed. Crystal laser cutters are the most powerful machine but also the most expensive.
Types of Laser Cutting
CO2 Laser Cutting
CO2 laser cutting is the most common type of laser cutting. CO2 lasers use carbon dioxide, nitrogen, and helium gas. The carbon dioxide helps to absorb the energy from the laser, making it ideal for cutting materials like wood, plastic, and glass. CO2 lasers are available at various levels, from low-power desktop units to industrial machines.
Fiber Laser Cutting
Fiber laser cutting is a newer technology that is becoming increasingly popular for cutting metals. Fiber lasers use a fiber optic cable to deliver the laser beam, which offers higher precision and speed than CO2 lasers. Fiber lasers are available at various levels, from low-power desktop units to high-power industrial machines.
Crystal Laser Cutting
Crystal laser cutting is the most potent type of laser cutting. Crystal lasers use a crystal to amplify the laser beam, making them ideal for cutting thick or rigid materials. Crystal lasers are available at various levels, from low-power desktop units to high-power industrial machines.
What are the Advantages of Laser Cutting?
There are many advantages to laser cutting, including:
Speed: Laser cutting is a fast process that can quickly produce large quantities of parts.
Precision: Laser cutters can produce precise and accurate cuts, making them ideal for applications where precision is essential.
Versatility: Laser cutters can cut various materials, including metal, wood, plastic, and glass.
What are the Disadvantages of Laser Cutting?
There are a few disadvantages to laser cutting, including:
Cost: Laser cutters are more expensive than other cutting machines, making them less ideal for large-scale production.
Material restrictions: Some materials, such as glass and ceramic, cannot be cut with a laser cutter.
Operator training: Laser cutters require operator training to ensure the machine is used correctly and safely.
What Can Materials be Cut with a Laser Cutter?
Laser cutters can be used to cut a variety of materials, including:
Metal: Laser cutters can be used to cut both ferrous and non-ferrous metals.
Wood: Laser cutters can be used to cut various wood types, including hardwoods and softwoods.
Plastic: Laser cutters can be used to cut a variety of plastics, including acrylic and polycarbonate.
Glass: Laser cutters can be used to cut glass, but special care must be taken to avoid shattering.
What are the Safety Precautions for Laser Cutting?
Laser cutting is a safe process when proper safety precautions are followed. Some of the safety precautions that should be taken when using a laser cutter include:
Wearing eye protection: Laser beams can harm the eyes, so wearing safety glasses or a face shield is essential when operating a laser cutter.
Avoiding reflective materials: Reflective materials, such as mirrors and metal, can reflect the laser beam and cause damage to the machine or operator. It is essential to avoid using reflective materials near the laser cutter.
Using ventilation: Laser cutting produces fumes and smoke, so it is essential to use ventilation to remove these contaminants from the workspace.
Plasma Cutting
Plasma cutting is a process that uses a hot plasma jet to cut through electrically conductive materials. Plasma cutting is fast, efficient, and accurate, making it ideal for various applications.
Plasma cutting creates an electrical arc between an electrode and the workpiece. This arc ionizes the gas in the plasma cutter, creating a hot plasma jet. The plasma jet is then directed at the workpiece, cutting through it as it goes.
Plasma cutting is a versatile technology used to cut various materials, including metal, wood, plastic, and glass. It can create simple and complex shapes, making it ideal for everything from prototyping to full-scale production.
Read Also: Why Walking Boots are Important for Travelers
What Can Materials be Cut with a Plasma Cutter?
Plasma cutters can be used to cut a variety of materials, including:
Metal: Plasma cutters can be used to cut both ferrous and non-ferrous metals.
Wood: Plasma cutters can be used to cut various wood types, including hardwoods and softwoods.
Plastic: Plasma cutters can be used to cut a variety of plastics, including acrylic and polycarbonate.
Glass: Plasma cutters can be used to cut glass, but special care must be taken to avoid shattering.
What are the Safety Precautions for Plasma Cutting?
Plasma cutting is a safe process when proper safety precautions are followed. Some of the safety precautions that should be taken when using a plasma cutter include:
Wearing eye protection: Plasma beams can harm the eyes, so it is essential to wear safety glasses or a face shield when operating a plasma cutter.
Avoiding reflective materials: Reflective materials, such as mirrors and metal, can reflect the plasma beam and cause damage to the machine or operator. It is essential to avoid using reflective materials near the plasma cutter.
Using ventilation: Plasma cutting produces fumes and smoke, so it is essential to use ventilation to remove these contaminants from the workspace.
Difference Between Laser cutting & Plasma Cutting
There are a few key differences between laser cutting and plasma cutting:
- Plasma cutting is typically faster than laser cutting, making it ideal for large-scale production.
- Laser cutting produces a cleaner than plasma cutting, making it ideal for applications where precision is essential.
- Plasma cutting can be used in a broader range of materials than laser cutting, including metal, wood, plastic, and glass.
- Laser cutting is more expensive than plasma cutting, making it less ideal for large-scale production.
CNC laser cutter
A CNC laser cutter is a CNC machine that uses a laser to cut materials. CNC stands for computer numerical control, and these machines are controlled by a computer that tells the laser where to cut.
CNC laser cutters are versatile and can cut various materials, including metal, wood, plastic, and even glass. They can be used to create both simple and complex shapes, making them ideal for everything from prototyping to full-scale production.
CNC laser cutters are more expensive than traditional laser cutters. Still, they offer several advantages, including increased accuracy and precision and the ability to create more complex shapes.
How Does it Work?
The working principle of the fiber laser cutter is quite simple. It all starts with an electric current passed through a tube filled with rare earth metals, which amplifies the light produced by the laser. This amplified light is passed through a lens, which focuses it into a small, powerful beam.
This beam is then directed at the material that is being cut, and the laser starts to do its work. As the beam comes into contact with the material, it starts to heat up. This heat eventually reaches a point where it is hot enough to vaporize the material, cutting through it cleanly and quickly.
A fiber laser cutter is a versatile tool that can be used to cut various materials, including metal, wood, plastic, and even glass. It can create simple and complex shapes, making it ideal for everything from prototyping to full-scale production.
Fiber laser cutters are more expensive than traditional laser cutters. Still, they offer several advantages, including increased accuracy and precision and the ability to create more complex shapes.
Conclusion
Plasma cutting and laser cutting are both versatile manufacturing processes that have a variety of applications. Plasma cutting is typically faster than laser cutting, making it ideal for large-scale production. Laser cutting produces a cleaner cut than plasma cutting, making it ideal for applications where precision is essential. Plasma cutting can be used in a broader range of materials than laser cutting, including metal, wood, plastic, and glass. Laser cutting is more expensive than plasma cutting, making it less ideal for large-scale production.